The lab grown diamonds debate rages on, sparking passionate discussions among consumers, jewelers, and environmentalists alike. This exploration delves into the complex world of synthetic gems, comparing them to their mined counterparts across environmental, economic, ethical, and technological factors. From the fascinating process of creating lab-grown diamonds to the evolving consumer perception, we’ll dissect the arguments for and against this burgeoning industry.
The debate centers around the relative merits of two production methods. Mined diamonds, historically the standard, involve extracting gems from the earth, a process with a long and often controversial history. Lab-grown diamonds, on the other hand, utilize sophisticated technologies to create diamonds in controlled laboratory environments. The resulting gems are indistinguishable from mined stones in many cases, yet their production methods are vastly different, leading to differing environmental and economic outcomes.
Introduction to Lab-Grown Diamonds

Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic diamonds, are man-made gemstones that possess the same chemical composition and physical properties as naturally occurring diamonds. They are created in a controlled laboratory environment, rather than formed deep within the Earth over millions of years. This process allows for greater control over the quality and characteristics of the diamonds, often leading to more consistent results and potentially lower prices than mined diamonds.The process of creating lab-grown diamonds involves several key steps and technologies.
A key aspect is the precise control of the growing environment, which is crucial to achieving the desired crystal structure and characteristics. Different methods exist, each with unique strengths and limitations.Historical context highlights the significant evolution of lab-grown diamond production. Initially, lab-grown diamonds were largely viewed as scientific curiosities, but advancements in technology and improved understanding of diamond formation led to increasing commercial production.
This contrasts with the long history of mined diamonds, often associated with significant historical and cultural events.Notable companies involved in lab-grown diamond production include Element Six, De Beers, and numerous smaller, specialized labs. These companies leverage innovative technologies to bring their diamonds to market.
Comparison of Lab-Grown and Mined Diamonds
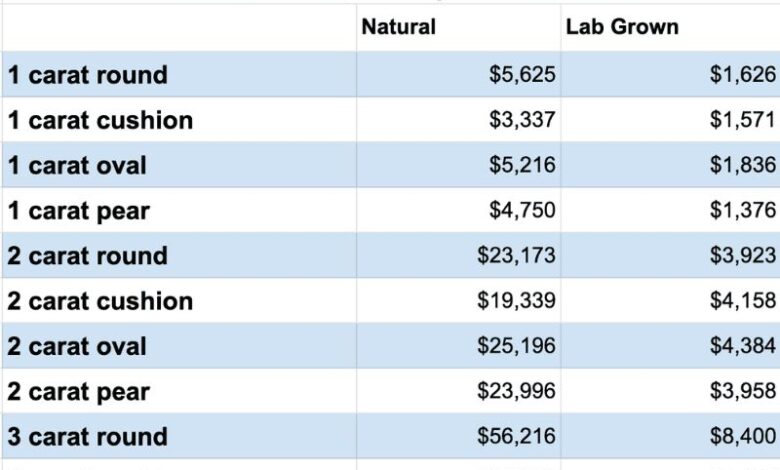
A comparison of key characteristics between lab-grown and mined diamonds reveals notable differences. The table below Artikels these distinctions.
The lab-grown diamond debate is heating up, isn’t it? It’s fascinating how ethical sourcing and environmental impact are now major factors in jewelry choices. But have you seen the incredible style evolution of Kaia Gerber and Cindy Crawford? Their mother-daughter style evolution, as detailed in this article , is truly inspiring. Ultimately, the lab-grown diamond debate boils down to personal values and preferences, just like choosing between Kaia and Cindy’s fashion statements.
| Characteristic | Lab-Grown Diamond | Mined Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Source | Typically, high-purity carbon in the form of gas or powder. | Carbon extracted from the Earth’s mantle. |
| Formation Process | Created under carefully controlled conditions in a laboratory environment using various techniques like high-pressure/high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). | Formed under immense pressure and temperature deep within the Earth. |
| Cost | Generally lower than mined diamonds, due to reduced production costs. | Often higher due to mining, processing, and marketing expenses. |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower environmental impact due to reduced mining activities and lower energy consumption in some cases. | Potentially higher environmental impact due to mining activities, transportation, and potential water usage. |
| Purity and Quality | Can be tailored to specific specifications. | Quality varies significantly based on natural geological processes. |
Lab-Grown Diamond Production Techniques
Several methods are used in the production of lab-grown diamonds, each with unique advantages and limitations.
- High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) Method: This method mimics the natural conditions of diamond formation deep within the Earth. The process involves heating and compressing carbon sources to high pressures and temperatures, allowing the carbon to crystallize into diamonds.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Method: In this method, gases containing carbon are introduced into a heated chamber. These gases react and deposit carbon atoms onto a seed crystal, gradually building the diamond. This method often results in smaller, but potentially more colourful, diamonds.
These methods provide precise control over the diamond-growing process.
Environmental Impact Debate
The allure of a sparkling diamond often overshadows the intricate environmental footprint of its creation. Whether mined from the earth or cultivated in a lab, the production process leaves its mark on the planet. Understanding these impacts is crucial for making informed decisions about our consumption choices.The environmental consequences of diamond mining are multifaceted and often severe. Land degradation, water pollution, and energy consumption are significant concerns.
The lab-grown diamond debate is heating up, with some arguing about their ethical and environmental impact. However, the glittering world of high fashion, exemplified by the Roberto Cavalli and Fausto Puglisi dinner party featured in Vogue’s 100, roberto cavalli fausto puglisi dinner party vogue100 , often prioritizes beauty and extravagance over origins, prompting a broader question about our values when it comes to luxury items.
Ultimately, the lab-grown diamond debate, like the fashion world itself, is a fascinating exploration of human choices and desires.
These practices frequently disrupt ecosystems, threaten biodiversity, and create long-lasting environmental damage. Conversely, lab-grown diamonds offer a potentially more sustainable alternative.
Diamond Mining Impacts
Diamond mining operations, often situated in remote and fragile ecosystems, significantly impact the environment. The extraction process involves large-scale excavation, altering the landscape and leading to soil erosion and habitat loss. The mining process can also introduce harmful chemicals into surrounding water sources, contaminating water supplies and harming aquatic life. Moreover, the energy required for mining, transportation, and processing diamonds contributes to overall carbon emissions.
Lab-Grown Diamond Impacts
Lab-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are produced using controlled laboratory environments. While energy is required for the process, the environmental impact is significantly different from that of traditional mining. A crucial factor is the energy consumption involved in heating, cooling, and operating the specialized equipment used in lab-grown diamond production. The waste generation from this process is another key consideration.
Proper management of byproducts and waste materials is crucial for responsible lab-grown diamond production.
Comparative Environmental Footprint
The environmental impact of mined and lab-grown diamonds differs considerably. Mining often involves substantial land disruption, water pollution, and significant carbon emissions. Conversely, lab-grown diamonds typically have a lower environmental footprint in terms of land use, water consumption, and air pollution, though energy consumption is a concern. The choice between the two methods depends on the specific environmental considerations.
Mitigation Solutions
Reducing the environmental impact of both mined and lab-grown diamonds requires a multi-pronged approach. For mining, stricter regulations, sustainable mining practices, and responsible water management are critical. These practices can minimize land degradation, reduce water pollution, and optimize energy consumption. For lab-grown diamonds, investing in renewable energy sources for production, developing sustainable waste management strategies, and promoting transparency in the supply chain are crucial steps.
A balanced approach that acknowledges the specific challenges of each method is essential for mitigating environmental harm.
Environmental Impact Comparison
| Factor | Mined Diamonds | Lab-Grown Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Land Disruption | High | Low |
| Water Usage | High (often contaminated) | Moderate |
| Carbon Emissions | High (mining, transportation) | Moderate (depending on energy source) |
| Waste Generation | High (mining waste) | Moderate (byproducts) |
| Biodiversity Impact | High (habitat loss) | Low |
Economic Considerations
The burgeoning lab-grown diamond industry presents a compelling economic case, contrasting sharply with the established mined diamond market. Examining the economic benefits and impacts of both sectors reveals significant differences in their resource utilization, environmental footprints, and, crucially, their potential for future growth. Understanding these nuances is essential to assessing the long-term implications of this transformative shift in the diamond market.This analysis delves into the economic ramifications of lab-grown diamonds, scrutinizing job creation, market growth, and pricing strategies.
Furthermore, it compares the economic models of both industries, highlighting the potential impact of lab-grown diamonds on the established mined diamond market.
Lab-Grown Diamond Industry Economic Benefits
The lab-grown diamond industry boasts a distinctive economic model, fostering innovation and driving market expansion. The controlled environment of laboratories allows for greater efficiency in production, reducing the cost of materials and manufacturing, which translates into more competitive pricing for consumers.
- Job Creation: The growing demand for lab-grown diamonds fuels the creation of new jobs across the supply chain, from laboratory technicians and engineers to marketing and sales professionals. This expansion creates new opportunities in sectors like technological research and development, which in turn strengthens the overall economy.
- Market Growth: The lower production costs and innovative designs associated with lab-grown diamonds lead to increased market share and a broader customer base. The industry’s adaptability to consumer trends and preferences positions it for continued growth and expansion, offering diverse product lines and price points.
Mined Diamond Industry Economic Impact
The mined diamond industry has a long history and significant economic impact, but faces evolving market dynamics. Its revenue generation and job creation are closely tied to the global demand for these precious stones.
- Job Creation and Revenue Generation: The mining sector provides jobs across various facets, from extraction and processing to distribution and retail. Revenue generation is substantial, supporting communities and economies in diamond-producing regions. The industry’s contribution to GDP and employment figures is noteworthy.
- Market Share: The mined diamond industry maintains a substantial market share, although the emergence of lab-grown diamonds poses a growing challenge to its traditional dominance. The industry’s response to this evolving market environment will determine its future success.
Comparative Economic Models
The economic models of the lab-grown and mined diamond industries differ significantly. Lab-grown diamonds leverage technological advancements and streamlined production processes, resulting in a potentially lower environmental impact and a more accessible price point. Mined diamonds, on the other hand, rely on traditional extraction methods and are often associated with significant environmental consequences.
Pricing Strategies
Both industries employ distinct pricing strategies. Lab-grown diamonds often utilize a more cost-effective approach, allowing for competitive pricing and broader accessibility. Mined diamonds, often perceived as a luxury commodity, employ strategies that reflect their perceived rarity and exclusivity.
Potential Economic Implications Table
| Economic Factor | Lab-Grown Diamonds | Mined Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Job Creation | Potential for substantial growth in new industries. | Likely to experience shifts in employment, potentially requiring adaptation. |
| Market Growth | Significant expansion potential, driven by accessibility and innovation. | Potential for market share erosion, necessitating innovation and adaptation. |
| Pricing | Competitive pricing, encouraging wider adoption. | Premium pricing strategy, potentially vulnerable to competition. |
| Revenue Generation | Growth in revenue generation linked to market expansion. | Revenue stability contingent on maintaining market share. |
| Environmental Impact | Generally lower environmental impact compared to mined diamonds. | Significant environmental impact from mining activities. |
Ethical Considerations
Diamonds, whether mined or lab-grown, have a complex relationship with ethical concerns. The pursuit of these sparkling gems often touches upon issues of labor practices, human rights, and environmental sustainability. Understanding these concerns is crucial for consumers seeking to align their purchasing decisions with their values. This section delves into the ethical landscapes surrounding both mined and lab-grown diamonds, examining the similarities and differences in their ethical frameworks.The ethical implications of diamond production extend beyond the glitz and glamour.
From the harsh realities of mining operations to the potential for exploitation in the supply chain, the industry’s history is fraught with challenges. Conversely, the lab-grown diamond industry presents a unique set of ethical considerations, demanding transparency and fair labor practices to ensure its ethical production aligns with consumer expectations.
Diamond Mining Ethical Concerns
The extraction of mined diamonds often raises serious concerns regarding labor practices and human rights. Many diamond mines, particularly in developing countries, have faced accusations of exploitative labor conditions. These include low wages, long working hours, unsafe working environments, and the use of child labor. Furthermore, the environmental impact of mining operations can include deforestation, water pollution, and habitat destruction.
These factors significantly impact local communities and ecosystems.
- Forced Labor and Child Labor: Reports of forced labor and child labor in some diamond mines have brought significant ethical concerns to light. Such practices violate fundamental human rights and are unacceptable in the modern world. Examples include cases where workers are held against their will or where children are employed in dangerous conditions. These instances highlight the urgent need for stricter oversight and enforcement of labor standards within the diamond mining industry.
- Fair Wages and Working Conditions: Many mining operations struggle to provide fair wages and safe working conditions for their employees. These factors contribute to significant disparities between the value of the product and the compensation received by those involved in its production. Addressing these issues is essential for ensuring a more equitable distribution of benefits.
- Environmental Damage: Diamond mining operations often result in substantial environmental damage, affecting local ecosystems. The process of extracting diamonds can lead to deforestation, water pollution, and the disruption of local wildlife habitats. This environmental impact is a major concern for stakeholders who prioritize sustainability and environmental protection.
Lab-Grown Diamond Ethical Concerns
The lab-grown diamond industry, while offering an alternative to mined diamonds, is not without its ethical challenges. Transparency in the supply chain and fair labor practices in the manufacturing processes are crucial. Concerns often arise regarding the environmental impact of the energy used in the lab-growth process and the potential for unethical labor practices in the supporting industries.
- Transparency and Traceability: The lack of transparency in the lab-grown diamond supply chain can pose ethical concerns. It’s challenging to track the origin of materials and ensure ethical sourcing throughout the entire production process. This lack of traceability can hinder efforts to identify and address any potential ethical issues within the industry.
- Energy Consumption: The energy consumption of lab-grown diamond production varies depending on the technology used. This energy consumption can have an environmental impact, requiring careful consideration and potentially impacting the overall sustainability of the process. Furthermore, the reliance on specific energy sources can raise further ethical concerns.
- Fair Labor Practices in Support Industries: Lab-grown diamond production relies on a complex network of support industries, such as equipment manufacturing, material supply, and logistics. Ensuring fair labor practices in these industries is essential to maintain the ethical integrity of the entire process.
Certification and Standards
Certification and industry standards play a crucial role in addressing ethical concerns in both the mined and lab-grown diamond industries. These standards help to ensure responsible sourcing, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability. Third-party certifications and ethical guidelines can help consumers and businesses make informed decisions, supporting more ethical practices.
- Role of Certification Bodies: Certification bodies play a critical role in establishing and enforcing standards for both mined and lab-grown diamonds. These bodies often provide independent audits and certifications to verify compliance with established ethical guidelines.
- Importance of Standards: Clear and universally recognized standards are essential for the diamond industry. These standards provide a benchmark for ethical practices, ensuring consistency and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Comparison of Ethical Frameworks
| Characteristic | Mined Diamonds | Lab-Grown Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Practices | Often criticized for exploitative labor conditions, including low wages, unsafe working environments, and human rights violations. | Potential for exploitative labor practices in support industries, but generally considered to have better labor conditions than mining operations. |
| Environmental Impact | Significant environmental impact due to mining operations. | Varying environmental impact depending on energy sources and manufacturing processes. |
| Transparency | Often opaque supply chains, making it difficult to trace the origin of diamonds and identify potential ethical concerns. | Potential for greater transparency in supply chains due to the controlled nature of lab-growth. |
| Certification | Increasingly adopting industry standards and certifications to address ethical concerns. | Growing adoption of industry standards and certifications, but still evolving. |
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Lab-grown diamonds are rapidly gaining traction in the market, challenging the traditional perception of mined diamonds as the ultimate luxury. This shift is driven by a confluence of factors, including evolving consumer values, technological advancements, and aggressive marketing strategies. Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing the origin and impact of their purchases, leading to a growing interest in sustainable and ethical alternatives.
Evolving Consumer Perception of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Consumer perception of lab-grown diamonds is undergoing a significant transformation. Factors influencing consumer choices include environmental consciousness, ethical concerns regarding mined diamond extraction, and the perceived value proposition of lab-grown diamonds. A key driver is the growing awareness of the environmental impact of mining and the potential for human rights abuses associated with some diamond mines. Additionally, the transparency and traceability offered by lab-grown diamond producers are contributing to a positive image.
The perceived value, often lower than mined diamonds, also attracts a wider customer base.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choices
Several factors contribute to the growing consumer preference for lab-grown diamonds. These include:
- Environmental Concerns: Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of mining, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Lab-grown diamonds, produced with significantly lower environmental footprints, resonate with this growing environmental consciousness.
- Ethical Concerns: Concerns about the labor practices and human rights issues in some diamond mines are driving demand for ethical alternatives. Lab-grown diamonds, often produced in controlled environments, offer a more transparent and traceable supply chain, appealing to ethically conscious consumers.
- Value Proposition: Lab-grown diamonds offer a compelling value proposition. Their lower production costs often translate to more affordable prices, making them accessible to a broader customer base compared to mined diamonds.
- Transparency and Traceability: The transparency of the lab-grown diamond production process, from the initial materials to the final product, fosters trust among consumers. This traceability is absent in the traditionally opaque mined diamond market.
Market Trends in the Lab-Grown Diamond Industry
The lab-grown diamond industry is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by increasing demand and aggressive competition. This growth is driven by innovative production methods, the expanding range of lab-grown diamond shapes and qualities, and a sophisticated marketing approach. New technologies are also improving the efficiency and affordability of lab-grown diamond production, creating a more competitive market.
Demand and Competition, Lab grown diamonds debate
Demand for lab-grown diamonds is significantly increasing, driven by factors such as affordability, ethical considerations, and the growing acceptance of these synthetic gems. Competition within the industry is fierce, with established companies and emerging players vying for market share. This competition is pushing companies to innovate, improve efficiency, and differentiate their offerings to capture a wider customer base.
Comparison of Consumer Demand for Lab-Grown and Mined Diamonds
The demand for lab-grown diamonds is steadily increasing, while the demand for mined diamonds, although still substantial, is experiencing a slight decline in certain segments. This shift is attributed to the rising awareness of ethical and environmental concerns surrounding mined diamonds. The value proposition of lab-grown diamonds, with their competitive pricing and ethical production, is drawing customers away from mined diamonds.
Marketing Strategies Employed by Both Industries
Both mined and lab-grown diamond companies employ various marketing strategies to promote their products. Mined diamond companies often focus on emphasizing the “forever” quality and tradition associated with mined diamonds. They also leverage celebrity endorsements and extravagant advertising campaigns to establish their brand image. Lab-grown diamond companies emphasize the sustainability, ethical sourcing, and affordability of their diamonds, promoting transparency and traceability through their marketing efforts.
Market Trends, Consumer Preferences, and Pricing Comparisons
| Factor | Lab-Grown Diamonds | Mined Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Market Trend | Rapid growth, increasing demand, fierce competition | Stable demand, but experiencing a decline in some segments |
| Consumer Preference | Sustainability, ethics, affordability, transparency | Tradition, “forever” quality, luxury, status symbol |
| Pricing | Generally lower than mined diamonds | Higher, reflecting scarcity and perceived value |
Technological Advancements: Lab Grown Diamonds Debate
The relentless pursuit of innovation in the lab-grown diamond industry is driven by the desire to enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of these synthetic gems. Technological advancements are rapidly reshaping the landscape, influencing both the manufacturing process and the overall diamond market. These developments are not only altering the production methods but also impacting the sustainability and economic viability of the industry.
Recent Technological Advancements in Lab-Grown Diamond Production
Significant progress has been made in various areas of lab-grown diamond production. Advanced high-pressure/high-temperature (HPHT) systems are now capable of producing larger, more uniform crystals with fewer imperfections. These systems are crucial for producing high-quality diamonds, and improvements in their design and operation are a key driver of this industry’s progress. Innovations in catalyst materials and growth techniques are further enhancing crystal quality and yield.
Impact of Technological Improvements on Cost and Quality
Technological enhancements have led to significant reductions in the cost of producing lab-grown diamonds. Improvements in the HPHT process, for instance, allow for faster growth rates and higher yields, directly impacting the cost per carat. These advancements also translate into improved quality control. More precise temperature and pressure regulation during the growth process result in diamonds with fewer inclusions and improved clarity, leading to a higher perceived value for consumers.
Role of Technology in Improving Efficiency and Sustainability
Technological progress is playing a critical role in enhancing both the efficiency and sustainability of lab-grown diamond production. Automated systems and robotic process control are optimizing production workflows, minimizing human error, and reducing overall production time. This translates to greater efficiency and potentially lower labor costs. In terms of sustainability, advancements in energy-efficient equipment are crucial for reducing the environmental footprint of diamond production.
The lab-grown diamond debate rages on, but perhaps the real “outdated” element here is the slow acceptance of innovation. Just like Vogue editors still champion some seriously dated fashion choices, like those described in this fascinating article about 9 outdated fashion pieces vogue editors still love , the hesitation to embrace lab-grown diamonds feels strangely similar. Ultimately, the quality and brilliance of lab-grown diamonds are undeniable, and the debate should center around accessibility and sustainability, not the perceived “vintage” aesthetic.
Impact of Technology on the Overall Diamond Market
Technological advancements are reshaping the diamond market. The increased availability of high-quality, affordable lab-grown diamonds is challenging the traditional market dominance of mined diamonds. This competition is driving innovation in both industries, with mined diamond producers adapting to meet the new market realities. Consumers are also becoming more aware of the environmental and ethical considerations surrounding both mined and lab-grown diamonds, which further shapes the market dynamics.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on the Diamond Industry
| Technological Advancement | Impact on the Diamond Industry |
|---|---|
| Improved HPHT Systems | Reduced production costs, increased yield, higher quality diamonds |
| Advanced Catalyst Materials | Enhanced crystal quality, improved growth rates |
| Automated Systems and Robotics | Increased efficiency, reduced production time, lower labor costs |
| Energy-Efficient Equipment | Reduced environmental footprint, lower operational costs |
| Improved Quality Control Methods | Enhanced clarity, fewer inclusions, higher perceived value |
Future Outlook
The lab-grown diamond market is experiencing rapid growth, posing both opportunities and challenges for the traditional mined diamond industry. Predicting the future involves considering factors like consumer preferences, technological advancements, and the evolving economic landscape. The interplay between these forces will shape the long-term trajectory of both segments.
Potential Future Trends in the Lab-Grown Diamond Market
The lab-grown diamond market is poised for continued expansion, driven by several factors. Increasing consumer awareness of lab-grown diamonds’ ethical and environmental benefits will likely fuel demand. Technological advancements will lead to even more affordable and accessible lab-grown options, potentially making them a viable alternative for a wider range of consumers.
Possible Future Impact on the Mined Diamond Industry
The rise of lab-grown diamonds presents a significant challenge to the traditional mined diamond industry. This challenge is multifaceted, impacting pricing strategies, marketing approaches, and the very perception of mined diamonds. The industry may need to adapt by emphasizing the unique qualities and provenance of mined stones, positioning them as luxury items with a history and rarity.
Potential Innovations in Both Industries
Both lab-grown and mined diamond industries are expected to innovate. In the lab-grown sector, innovations could focus on producing diamonds with unique colors, sizes, and cuts, further differentiating them from mined diamonds. The mined diamond industry might focus on sustainable mining practices, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing transparency in the supply chain.
Forecast for the Future of Both Types of Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are projected to continue their strong growth trajectory, particularly in the lower price segment. This is due to their competitive pricing and increasing consumer acceptance. Mined diamonds, on the other hand, are likely to maintain their position in the high-end market, relying on their inherent rarity and historical significance. The future will likely see a coexistence of both, with each sector catering to different consumer needs and preferences.
Table of Possible Future Scenarios and Predictions
| Scenario | Lab-Grown Diamond Market | Mined Diamond Market | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continued Growth | Significant expansion in market share, particularly in the lower price range. Wider availability and affordability will drive increased demand. | Maintains a significant presence in the high-end market. Emphasis on unique qualities and heritage. | A co-existing market where both types of diamonds cater to different consumer segments. |
| Disruption | Significant market penetration, potentially impacting the demand for mined diamonds in the mid-range price segment. | Pressure to innovate and adapt, including exploration of new marketing strategies. | Potential for market consolidation, with the dominant player in the market depending on consumer preferences and technological advances. |
| Symbiotic Relationship | Lab-grown diamonds become a key competitor to mined diamonds, but both segments coexist, catering to diverse needs. | Mined diamonds continue to appeal to consumers seeking authenticity and rarity. | A sustainable coexistence, where both types of diamonds find their place in the market. |
Conclusion
Ultimately, the lab grown diamonds debate highlights a fundamental shift in the jewelry industry. As technology advances and consumer preferences evolve, the question of sustainability, ethics, and cost-effectiveness becomes paramount. The comparison between lab-grown and mined diamonds offers a valuable lens through which to examine these complex issues. While both methods have their proponents and detractors, the ongoing discussion underscores the need for transparency, responsible practices, and a careful consideration of the full impact of our choices, especially when it comes to precious stones.

